New media technology, the increasing prevalence of linked cellular phones, and increased access to global information sources, along with social networking and media-sharing websites, has altered the way that individuals learn, interpret, create and ‘publish’ work. The Open Movement has evolved as individuals and institutions around the world have embraced the benefits of releasing digitised...
New media technology, the increasing prevalence of linked cellular phones, and increased access to global information sources, along with social networking and media-sharing websites, has altered the way that individuals learn, interpret, create and ‘publish’ work.
The Open Movement has evolved as individuals and institutions around the world have embraced the benefits of releasing digitised text and multi-media content that is online, free of charge, often collaborative, and free of most copyright and licensing restrictions. Their actions remove most of the barriers – commercial and access – to knowledge and creative content. It harnesses and develops social economy, and allows for innovative education and creative exchange and support.
The Open Movement incorporates Open Access, Open Data, Open Source, Open Science, Open Education, Open Licensing and Open Content. Notable information sources and approaches that are results of the Open Online Movement include Wikipedia, Creative Commons, Khan Academy, Open Knowledge Foundation, Wikimedia projects, Open Education Resources (OER – including MITx and Coursera) and citizen journalism[1].
[1]The concept of citizen journalism (also known as “public”, “participatory”, “democratic”, “guerrilla” or “street” journalism) is based upon public citizens “playing an active role in the process of collecting, reporting, analyzing, and disseminating news and information.” Citizen journalism should not be confused with community journalism or civic journalism, both of which are practiced by professional journalists. Collaborative journalism is also a separate concept and is the practice of professional and non-professional journalists working together. Citizen journalism is a specific form of both citizen media and user generated content.
WikiAfrica is an international movement that takes place on the African continent and beyond. It encourages individuals, interested groups and organisations to create, expand and enhance online content about Africa. This involves motivating for the representation of the continent’s contemporary realities and history, its peoples and its innovations on the world’s most used encyclopaedia, Wikipedia. WikiAfrica is not owned by one organisation and it belongs to all people and organisations contributing to its scope.
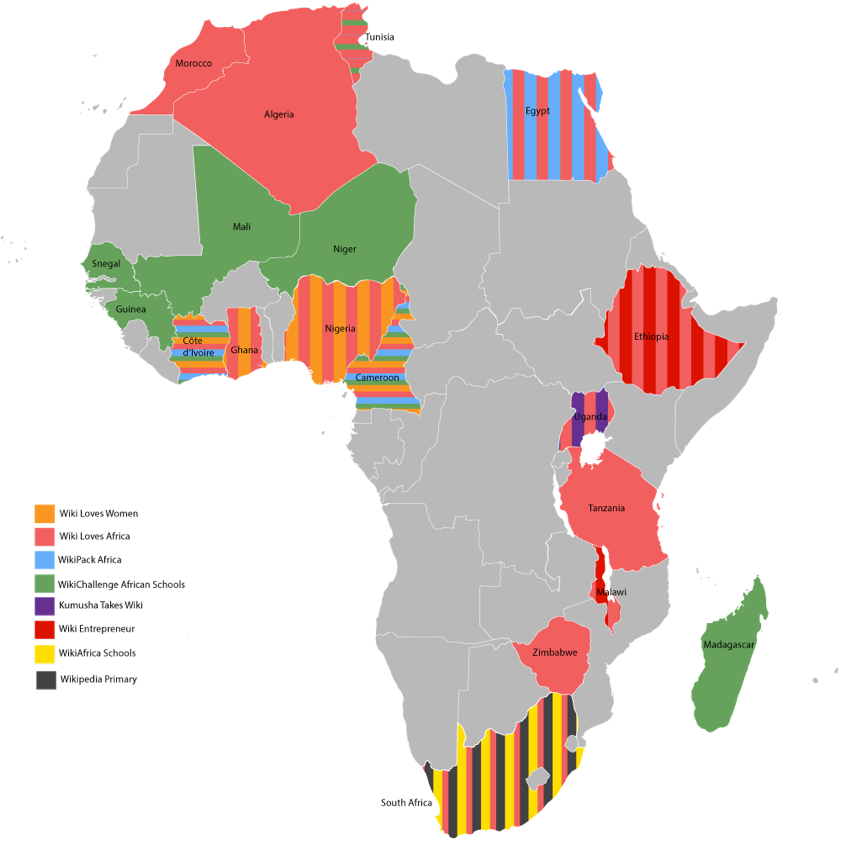
In its various guises and hosted at several institutions (including Lettera27, Africa Centre, Ynternet.org, and Wikimedia CH), the WikiAfrica movement has consistently instigated and led multi-faceted innovative projects. These projects have activated communities and driven content onto Wikipedia. Examples include Share Your Knowledge, #OpenAfrica training Courses and Toolkits, Kumusha Bus (in Ethiopia and Ghana), WikiEntrepreneur (in Ethiopia and Malawi), Kumusha Takes Wiki (Cote d’Ivoire and Uganda) and Wiki Loves Africa.
Over 2016/17 it is working on Wiki Loves Women (in collaboration with the Goethe-Institut), WikiPack Africa, WikiFundi and the WikiChallenge African Schools (funded by the Orange Foundation), WikiAfrica Schools (funded by lettera27), Wikipedia Primary (funded by SUPSI) and Wiki Loves Africa (funded by Wikimedia Foundation).
WikiAfrica was started in 2006 as a collaboration between Wikimedia IT and lettera27, since then – via the support of several organisations and the work of a few people – it has grown to embrace the continent and build communities. It has been pivotal in driving the current contributions done by communities across sub-Saharan Africa.
The projects detailed below form the main backbone of the WikiAfrica movement. They have all been conceptualised, instigated and led by three members of Wiki In Africa, although until 2017 through the agency or fiscal sponsorship of different organisations.
2006
2009
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
The organisations that have hosted or are collaborating on Wiki Africa projects include: